ChargePoint DC rapid chargers charge quicker than fast (AC) chargers and are easy to use. Like any fast charge ChargePoint charging station, just tap your phone or card, plug in to charge and then go on your way. The best time to use DC rapid charging is when you need a charge right away and you’re willing to pay a little more for the convenience — like on a road trip, or if you have a low battery but are pressed for time.
Check out these tips to get a great fast charging experience.
Tip: Not every EV is capable of DC rapid charging. If you think you’ll need a fast charge from time to time, make sure to ask about this option when buying your EV.
Check your car and connector type
DC rapid charging uses a different connector from the J1772 connector used for fast AC charging. Leading fast charging standards are SAE Combo (CCS1 in the U.S. and CCS2 in Europe), CHAdeMO and Tesla (as well as GB/T in China). More and more cars are equipped for DC rapid charging these days, but be sure to take a quick look at your car's port before you try to plug in. Here's what some common connectors look like:
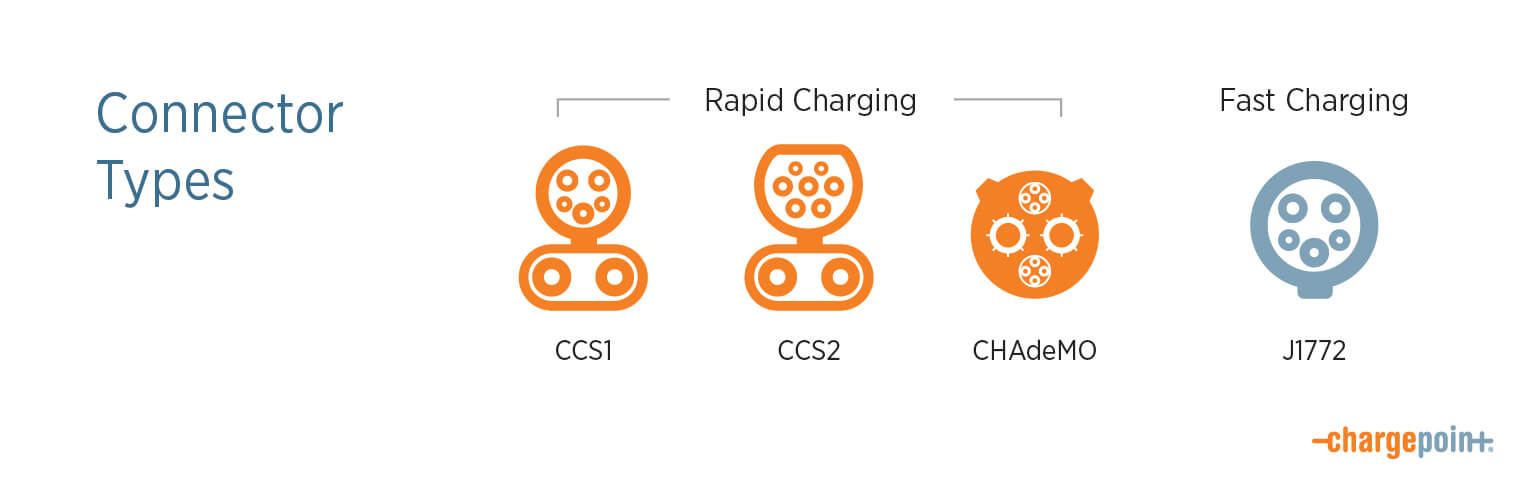
Tip: You can filter by connector type in the ChargePoint app to find stations that work for your EV.
Save rapid charging for when you need it most
Fees are usually higher for DC rapid charging than for AC fast charging. Because it provides more power, DC rapid is more expensive to install and operate. Keep in mind that particularly those drivers who don't have access to charging at home or work may rely more on DC rapid charging. To provide plenty of DC rapid charging capacity in cities and the countryside in the future, many European legislators are in the process of setting targets to ensure sufficient DC charging ahead of demand.
Follow the 80% rule
Every car battery follows what’s called a “charging curve” when charging. Charging starts slow while your car monitors several factors (from your battery’s charge level to the weather outside), climbs to peak speeds for as long as possible and slows down again at around 80% to prolong battery life. (We'll show you what these "charging curves" of charging speed look like in some upcoming posts.)
With a DC rapid charger, it’s best to unplug when your battery reaches about 80% charge. That’s when charging slows dramatically — it could take almost as long to fill the last 20% of charge as it did to get to 80% in the first place. Unplugging when you get to 80% charge is not only more efficient for you, it’s also considerate to other EV drivers and helps make sure that as many people as possible can use fast charging stations. Check the ChargePoint app to see how your charge is going and when to unplug.
Did you know? With the ChargePoint app, you can see the rate at which your car is charging in real time. Just click on Charging Activity in the main menu to see your current session.
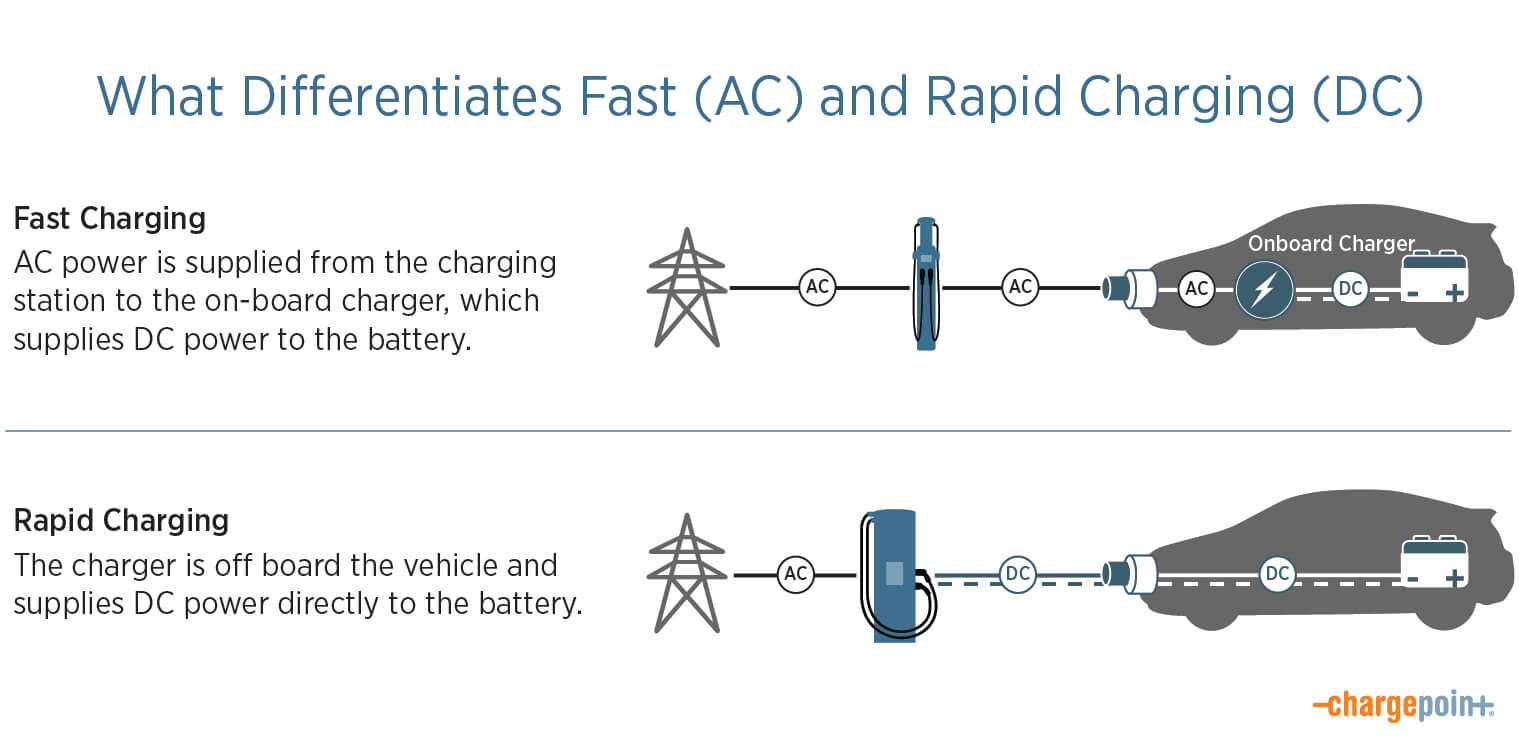
AC vs DC
Finally, if you’ve ever wondered why it’s called “DC rapid charging,” that answer is simple, too. “DC” refers to “direct current,” the type of power that batteries use. Fast charging stations use “AC,” or “alternating current,” which you’ll find in typical household outlets. EVs have “onboard chargers” inside the car that convert AC power to DC for the battery. DC rapid chargers convert AC power to DC within the charging station and deliver DC power directly to the battery, which is why they charge faster.
Our ChargePoint Express stations provide DC rapid charging. You can find a rapid charging spot that works for your car using the ChargePoint app.
Would you like to know more about the difference between AC fast charging and DC rapid charging? Then download our guide, which explains the different types of charging and when to best use them in more detail.



